Environmental Benefits of Jellyfish
Project by Students of Carleton University
Date: December 10th, 2021
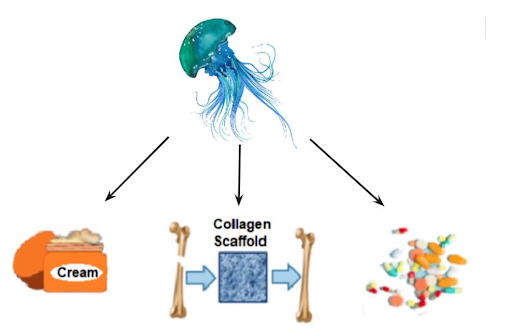
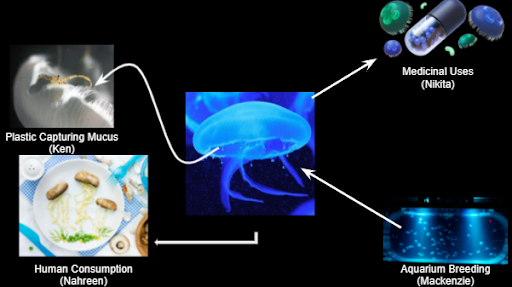
Our project begins with jellyfish! Jellyfish are very useful because of the three things they can provide us: cleaner waters, useful medicine and a sustainable food replacement. All of these things can be seen below in Figure 1, which shows the sub-topics our team has researched.
Figure 1: System sub-topics [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, modified]
We first got the idea to research jellyfish from a BBC video post which our professor shared with us [6]. The fact that jellyfish is such a versatile product, but yet seems so underused in our markets today piqued our group's interest.
Jellyfish can be used to clean plastic pollution out of our waters, they can provide a sustainable and responsible protein replacement in our diets and they can even provide us with crucial medicines that speed up patients' recoveries! We did not know that jellyfish could do all these things, and some of us even thought they were kind of gross, but after learning all these things we came to the conclusion that they might be an extremely useful tool for humanity's future success!
REFERENCES
[1] B. Gemmel, Moon Jellyfish With Oil & Mucus. Smithsonian [Website] https://ocean.si.edu/ocean-life/invertebrates/moon-jellyfish-oil-mucus [Accessed 16-Sept-2021]
[2] S. Ang Pixaby, Jellyfish: a mesmerizing menace. [Website] https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2019/01/how-an-explosion-of-jellyfish-is-wreaking-havoc/ [Accessed 17-Sept-2021]
[3] “Jellyfish Aquarium Maintenance”, Aquarium Services of Oregon. [Website]. Available:https://www.aquariumservicesoregon.com/jellyfish-aquarium-maintenance/. [Accessed 17-Sept-2021]
[4] Jellyfish Food Stock Photos. 2021 [Website] Available: https://www.dreamstime.com/photos-images/jellyfish-food.html [Accessed 19-Sept-2021].
[5] N. Madrid and C. Eisner, Americans Took Prevagen for Years—as the FDA Questioned Its Safety, October 21, 2020. [Online]. Available:
https://www.wired.com/story/prevagen-made-millions-fda-questioned-safety/
[6] R. Evans, D. Gordon and T. Heyden, “Microplastics, drugs and food - how jellyfish can help us”. BBC, 2021 [Online] Available: https://www.bbc.com/news/av/stories-55360696 [Accessed 17-Sept-2021]
Aquatic Microplastic Removal: Ken
Jellyfish mucus was found to have the ability to trap water-borne microplastics. Scientists have proposed that by using this property, jellyfish mucus could aid humanity in ridding the Earth’s waters of microplastic pollution which we have caused [1] Figure 2 below shows how jellyfish mucus trapping oil droplets like it would microplastics.
Figure 2: Jellyfish mucus trapping small oil-droplets in the same way it would trap microplastics [2]
Microplastics are small plastics which have either been manufactured to be small (think glitter) or which have broken down over time from larger products (for example a disposable plastic water bottle might break down over time in water, just as a rock face is eroded over time).
So, how does the jellyfish mucus actually attract and trap these microplastics? it comes down to the molecular composition of both the mucus and the microplastics. Intermolecular forces are the forces pulling the two together, but since there are many different intermolecular forces, it depends largely on the composition of the microplastics. In general, microplastics with a more “charged” molecular makeup will stick to jellyfish mucus. An example of such a plastic is PVC. PVC is a very common plastic, used in everything from food packaging to electrical products [3]. Overall, jellyfish mucus has a decent ability to trap microplastics, although it is not a catch-all solution, and other helpers would be needed to capture ALL microplastics.
REFERENCES
[1] A. Patwa, A. Thiery, F. Lombard, M. K.S. Lilley, C. Boisset, J.F. Bramard, J.Y. Bottero & P. Barthelemy, “Accumulation of nanoparticles in “jellyfish” mucus: a bio-inspired route to decontamination of nano-waste”. Scientific Reports, 2015. [online] Available: https://www.nature.com/articles/srep11387?dom=pscau&src=syn [Accessed October 19th, 2021]
[2] B. Gemmell, Jellyfish Mucus and Oil. Smithsonian [Website] Available: https://ocean.si.edu/holding-tank/images-hide/jellyfish-mucus-and-oil [Accessed 17-Sept-2021]
[3] “Polymers of Commercial Importance”. Toppr. [online] Available: https://www.toppr.com/guides/chemistry/polymers/polymers-of-commercial-importance/ [Accessed October 19th, 2021]
Edible Jellyfish: Nahreen
So we all know jellyfish sting. And we all know what they look like. But did you know that you can EAT jellyfish? And not just one specific jellyfish found in some ocean corner, but more than 30 species globally have been proven ‘safe-to-eat’ [1].
Jellyfish are made of water and protein, with few traces of fats and carbohydrates [2]. The main protein present in jellyfish is collagen. Collagen is a super important protein. They are found in our hair, skin, and muscles. Proteins help build the structural components of our cells, enzymes and hormones.
The human body is able to fully digest these proteins. Digestion is the mechanical and chemical breakdown of food into smaller chunks that our body can easily process [3]. Bigger pieces of food are harder for our body to work with since our cells are only able to absorb nutrients at a molecular level. Proteins are made up of smaller molecular substances called amino acids [4], held together by peptide bonds. An enzyme, pepsin, is released into the stomach, which breaks down the peptide bonds between the large protein chains into amino acids. This can be seen in Figure 3 below. Cells use amino acids to repair tissue, build muscle and transport nutrients to organs.
Fig 3: Sliced jellyfish[5]
Okay, that’s a lot of information. And a lot of facts, but what do I do with this information? Why are we talking about proteins in jellyfish? That's my question too, but slightly more...hungry. Can we eat jellyfish? Turns out, yes we can!
Jellyfish are presently only a delicacy within Asian countries but is slowly making its way to the western world. Around 7 million pounds of jellyfish are caught and harvested in the state of Georgia and shipped to Asian countries such as China, Korea and Japan[5]. In such Asian countries, the public consumes jellyfish as an appetizer, or as a part of a salad. Normally, we can eat only the Bell (or head) of Jellyfish. Its tentacles still cannot be processed since they're such intricate organs, these parts are either thrown away or fed to other animals.
So what do you think, would you try jellyfish?
REFERENCES
[1] A. Bourget, “Jellyfish: If you can't beat them, Eat Them,” Food, 01-Feb-2018. [Online]. Available:https://www.sbs.com.au/food/article/2018/02/01/jellyfish-if-you-cant-beat-them-eat-them. [Accessed: 17-Oct-2021].
[2]P. Gillam, “Digestion of proteins: Grade 9 understanding for IGCSE Biology 2.29 2.30 2.31,” PMG Biology, 14-Jul-2019. [Online]. Available: https://pmgbiology.com/2016/02/14/digestionof-lipids-a-understanding-for-igcse-biology-2-29/. [Accessed: 05-Oct-2021].
[3]L. Learning, “Biology for majors II,” Lumen. [Website]. Available: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wm-biology2/chapter/digestive-system-processes/.[Accessed: 20-Sep-2021].
[4]S. Kampshoff, "What are Proteins and What is Their Function in the Body?", Eufic.org, 2021.[Website].Available:https://www.eufic.org/en/whats-in-food/article/what-are-proteins-andwhat-is-their-function-in-the-body.[Accessed: 20- Sep- 2021].
[5]P. Wong, “How jellyfish is eaten in China - in season (S1E5),” YouTube, 15-Oct-2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aucEaNDoCRY&ab_channel=Goldthread.
[Accessed: 20-Oct-2021].
Medicinal Benefits of Jellyfish: Nikita
Did you know that the collagen present in jellyfish is used for manufacturing health and beauty supplements? Collagen is a protein that provides strength and structure to the bones, muscles and tendons of the human body and it helps to hold the body together by forming a scaffold [1]. Consuming health supplements containing collagen, as seen in figure 4, has many nutritional benefits [2]. Since jellyfish protein constitutes about 80 to 90 percent of collagen, they are one of the most sustainable sources of marine collagen [1].
Collagen has a wide variety of applications ranging from tissue regeneration to manufacturing of cosmetics and health supplements. Cosmetics made from collagen protects the skin from UV radiation by reducing the loss of moisture, thereby reducing the formation of wrinkles [3]. Collagen dressing also speeds up the tissue regeneration process by stimulating the body to produce collagen on its own and support the growth of new cells [4] as shown in figure 5 below. This in turn reduces the recovery time.
In order to use jellyfish collagen for these applications, it first needs to be extracted. The extraction of collagen is a two step process [5]. The collagen that is separated from jellyfish is thermally treated to produce gelatin [5]. This gelatin undergoes enzymatic hydrolysis where the collagen (substrate) breaks down in the presence of enzymes and water to produce collagen peptides [5]. These collagen peptides are used for different applications in the medical and pharmaceutical industry such as tissue reconstruction, to hinder wrinkles and for cosmetics.
Figure 4: Applications of jellyfish collagen [6]
REFERENCES
[1] C. Cobb, “What is collagen, and why do people use it?”, MedicalNewsToday, [Website], June 16, 2017. Available:
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/262881#:~:text=Collagen%20is%20the%20most%20abundant,to%20provide%20strength%20and%20structure. [Accessed Nov-17-2021]
[2]“Longevity breakthrough of the century”: Jellyfish collagen investigated for cognition”, nutrition insight, [Website], May 27, 2020. Available:
https://www.nutritioninsight.com/news/longevity-breakthrough-of-the-century-jellyfish-collagen-investigated-for-cognition.html.[Accessed Nov-17-2021]
[3] J. Fan,1 Y. Zhuang, B. Li, Effects of Collagen and Collagen Hydrolysate from Jellyfish Umbrella on Histological and Immunity Changes of Mice Photoaging, January 17. [Website]. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3571645/.[Accessed 12-Nov-2021].
[4] N. Marriott, “Jellagen launches jellyfish collagen manufacturing facility”, May 25, 2017. [Website]. Available: https://www.europeanpharmaceuticalreview.com/news/51664/jellagen-launches-jellyfish-collagen/. [Accessed 19-Oct-2021].
[5] D. Coppola, M. Oliviero, G.A Vitale et al. “Marine Collagen from Alternative and Sustainable Sources: Extraction, Processing and Application”, marine drugs, [online pdf], April 15, 2020,
https://www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/18/4/214/htm. [Accessed 10-Nov-2021].
[6] M. Yeomans, “Cosmetic industry use of jellyfish can help falling fish stocks to recover”, Cosmetics design.com, [Website], June 2, 2013. Available: https://www.cosmeticsdesign.com/Article/2013/06/03/Cosmetics-industry-use-of-jellyfish-can-help-falling-fish-stocks-to-recover. [Accessed 22-Nov-2021].
Breeding Jellyfish in Aquariums: Mackenzie
As we all know, jellyfish live in the ocean and if you’ve ever been in the ocean, you know that the water is pretty cold. The water in an aquarium for jellyfish needs to be the same temperature as the ocean in order for them to survive and breed. These conditions cannot be sustained in an aquarium without an aquarium chiller. An aquarium chiller can be thought of as a fancy air conditioner, but for water. It cools down aquariums using conduction heat transfer. Think of a time when you’ve gone to touch a frying pan and it was still hot. I bet you burnt your hand and this was because of the heat from the pan transferring to your hand, which is conduction. Conduction is the transfer of thermal energy (heat) through the direct contact of molecules [1]. The thermal energy transfers from the hot molecules to the cold molecules.
Now let’s dive into how the aquarium chiller works. The aquarium water flows within the aquarium chiller, where cooling coils surround the water – they are in direct contact [2], this can be seen in Figure 5, below. The coils contain cold refrigerant liquid, making the coils cold. The coils are colder than the water in the aquarium. Because the water and the coils are not the same temperature, the thermal equilibrium process begins through conduction. The warmer water transfers its thermal energy to the coils to reach thermal equilibrium. This causes the water to cool down to the desired temperature, getting rid of its excess heat by transferring it to the coils in the aquarium chiller. Just like that, the water is at the desired temperature and we’ve created ideal living conditions for jellyfish to live and breed in aquariums.
Figure 5: Inside an aquarium chiller [3, modified]
REFERENCES
[1] UCAR, “Conduction”, UCAR. [Website]. Available: https://scied.ucar.edu/learning-zone/earth-system/conduction. [Accessed 14-Sept-2021].
[2] C.Pardue, “Aquarium Chillers and How They Work”, Fragglereef. [Website]. Available: https://www.fragglereef.co.uk/aquarium-chillers-and-how-they-work/. [Accessed 14-Sept-2021].
[3] Online Water Chillers, Indian Mart. [Website]. Available : https://www.indiamart.com/proddetail/online-water-chillers-14123160573.html. [Accessed 30-Oct-2021]